 |
| Overview |
| News |
| Documentation |
| Screen shot |
| System Requirements |
| Download |
| Mailing Lists |
| References |
A UML-based Specification Environment | ||||||||||
| Overview | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
USE is a system for the specification of information systems. It is based on a subset of the Unified Modeling Language (UML) [1]. A USE specification contains a textual description of a model using features found in UML class diagrams (classes, associations, etc.). Expressions written in the Object Constraint Language (OCL) are used to specify additional integrity constraints on the model. A model can be animated to validate the specification against non-formal requirements. System states (snapshots of a running system) can be created and manipulated during an animation. For each snapshot the OCL constraints are automatically checked. Information about a system state is given by graphical views. OCL expressions can be entered and evaluated to query detailed information about a system state. The picture below gives a general view of the USE approach. 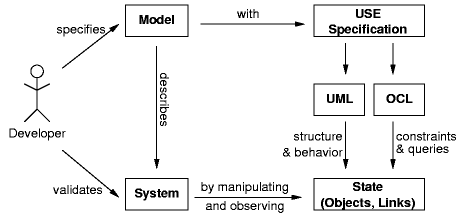 The USE specification language is based on UML and OCL. Due to the semi-formal definition of OCL there are some language constructs whose interpretation is ambiguous or unclear [2]. In [3] and [4] we have presented a formalization of OCL which attempts to provide a solution for most of the problems. The USE approach to validation is described in [5]. This is ongoing work and it is likely that there will be changes in USE. | ||||||||||
| News | ||||||||||
| ||||||||||
| Documentation | ||||||||||
|
The following documentation is available.
| ||||||||||
| Screen shot | ||||||||||
|
The screen shot below shows information about a system state generated with the USE tool. More detailed information is given in the quick tour. Click on the picture below to get an enlarged version. 
| ||||||||||
| System Requirements | ||||||||||
|
USE is implemented in Java(tm). It should run on any platform on which a Java runtime system (e.g. the Sun JDK) is available. So far this has been tested only on Unix-like platforms (Solaris and Linux) but it seems to work also on Windows. If you're trying to install USE on any other platform, you are on your own, although this should not be too difficult. To compile USE you will need Sun's Java Development Kit (JDK) version 1.2 or later (see http://java.sun.com). | ||||||||||
| Download | ||||||||||
|
Note that this is a preliminary release of a research prototype. There is no warranty of any kind. The release is available in compressed tar and jar format. Both files have the same content but the gzipped tar file is much smaller in size. Note that the file use-X.YY.jar is not a runnable Java class archive. You have to unpack it first using a command like jar xvf use-X.YY.jar (see your JDK docs for details). After unpacking the release archive, please read the files README and INSTALL for further information. If you are updating your USE release, please read the file NEWS. It contains a short summary of changes between releases.
Older releases are still available. | ||||||||||
| Mailing Lists | ||||||||||
|
There are two mailing lists related to USE. If you want to get notifications about new releases, you should subscribe to the list use-announce. This is a moderated list only used for announcements. The list use is for general discussions about USE. To subscribe to a list, send "subscribe" in the body of a message to the appropriate *-request address: To report problems with any of the mailing lists, send mail to owner-use@informatik.uni-bremen.de. | ||||||||||
| References | ||||||||||
|
See also the complete list of publications of our group where most papers are available online.
|